Insulation
Proper insulation provides resistance to heat flow, low heating and cooling costs, and comfort. The insulation you choose will be important for long-term efficiency.
Our Insulation Services
Blanket • Blow-In Retrofiitting • Sprayed Foam
Types of Insulation
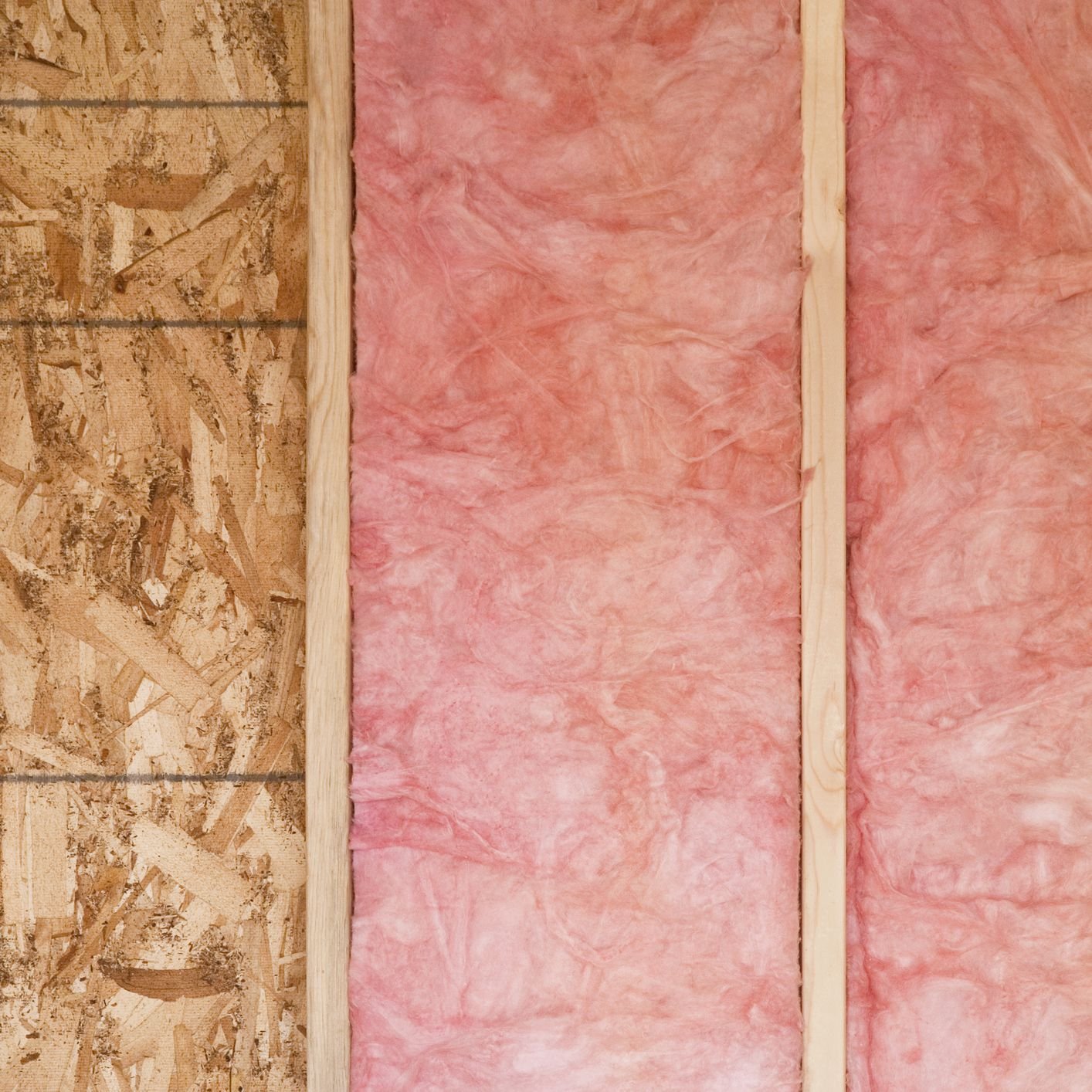
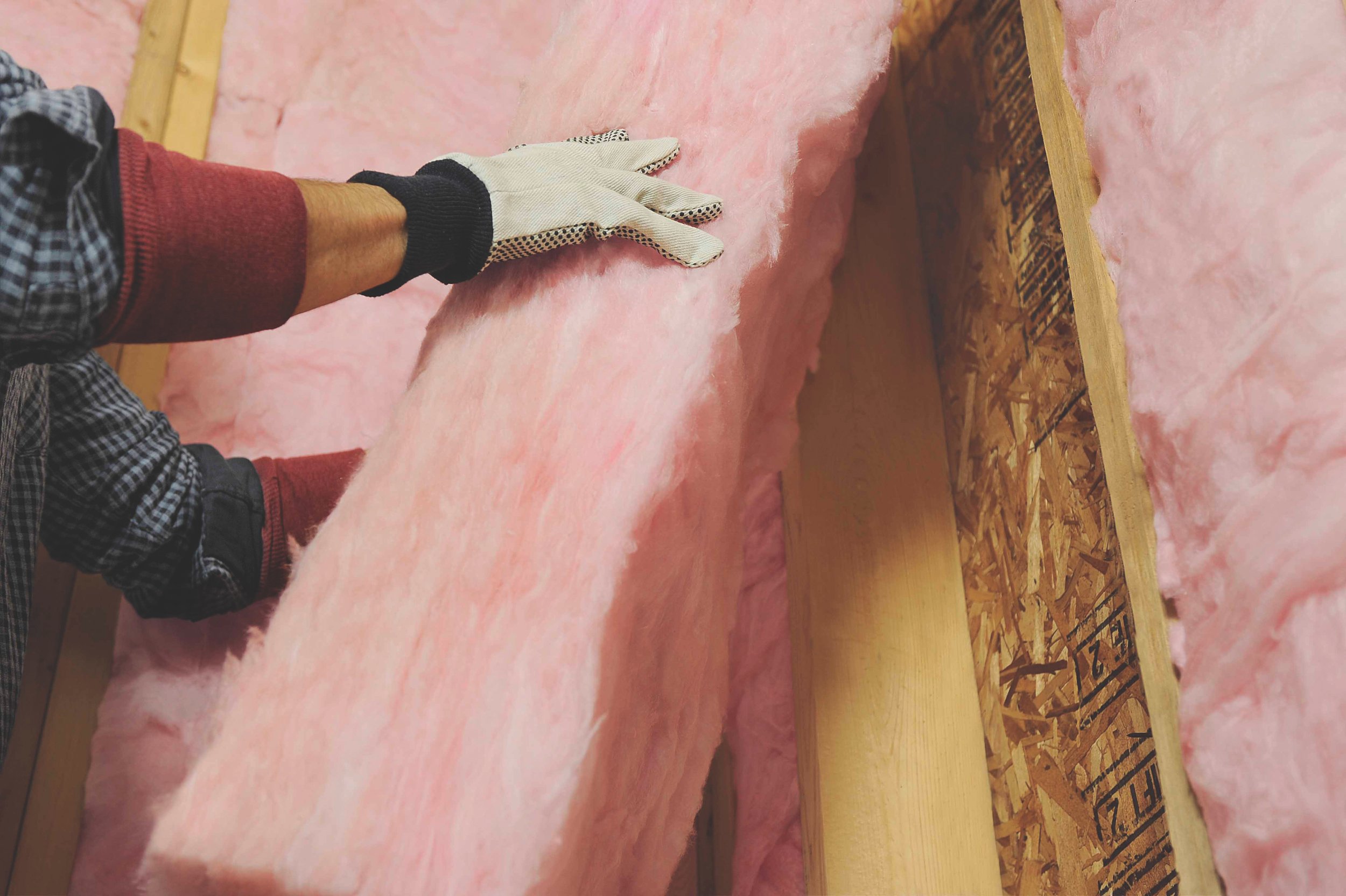
Blanket
Materials:
Fiberglass • Mineral Wool • Plastic Fibers • Natural Fibers
Where Applicable:
Unfinished Walls, including foundation walls • Floors and ceilings
Benefits :
Suited for standard stud and joist spacing that is relatively free from obstructions. Relatively inexpensive.
Concrete Block
Materials:
Foam board, to be placed on outside of wall (usually new construction) or inside of wall (existing homes): Some manufacturers incorporate foam beads or air into the concrete mix to increase R-values
Where Applicable:
Unfinished walls, including foundation walls • New construction • Major renovations • Walls (insulating concrete blocks)
Benefits :
Insulating cores increases wall R-value. Insulating outside of concrete block wall places mass inside conditioned space, which can moderate indoor temperatures.Autoclaved aerated concrete and autoclaved cellular concrete masonry units have 10 times the insulating value of conventional concrete.
Foam Board/Rigid Foam
Materials:
Polystyrene • Polyisocyanurate • Polyurethane • Phenolic
Where Applicable:
Unfinished Walls, including foundation walls • Floors and ceilings • Unvented Low-Slope Roofs
Benefits :
High insulating value for relatively little thickness. Can block thermal short circuits when installed continuously over frames or joists.
Insulating Concrete Forms (ICFs)
Materials:
Foam Boards • Foam Blocks
Where Applicable:
Unfinished Walls, including foundation walls for new construction
Benefits :
Insulation is literally built into the home's walls, creating high thermal resistance.
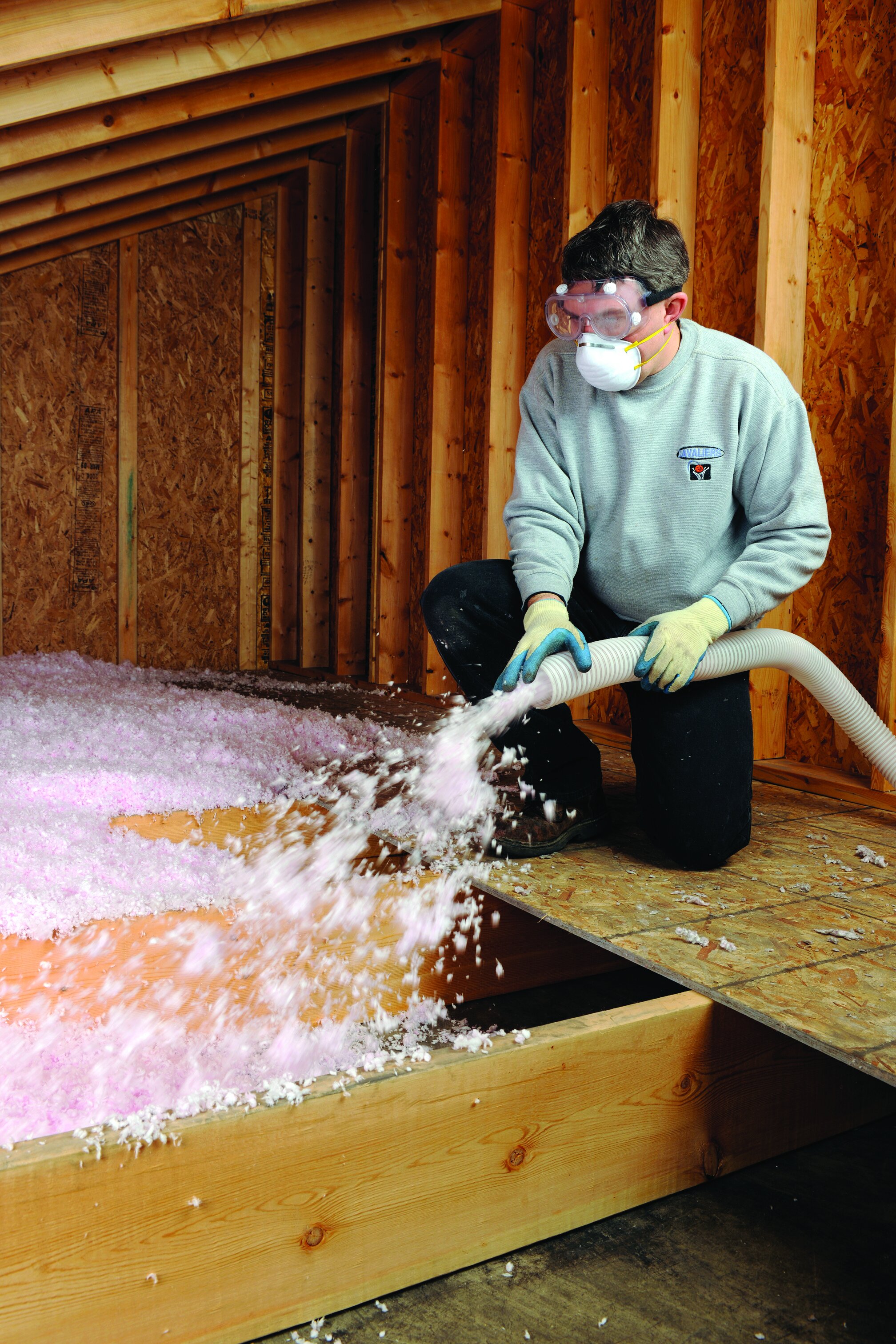
Loose-Fill/ Blown-In
Materials:
Cellulose • Fiberglass • Mineral Wool
Where Applicable:
Enclosed Existing Wall • Open New Wall Cavities • Unfinished Attic Floors • Other Hard-To-Reach Places
Benefits :
Good for adding insulation to existing finished areas, irregularly shaped areas, and around obstructions.
Reflective System
Materials:
Foil-Faced Kraft Paper • Plastic Film • Polyethylene Bubbles • Cardboard
Where Applicable:
Unfinished Walls, Ceilings, and Floors
Benefits :
Suitable for framing at standard spacing • Bubble-form suitable if framing is irregular or if obstructions are present • Most effective at preventing downward heat flow, effectiveness depends on spacing and number of foils.
Rigid Fibrous
Materials:
Fiberglass • Mineral Wool
Where Applicable:
Ducts in unconditioned spaces • Other places requiring insulation that can withstand high temperatures
Benefits :
Can withstand high temperatures
Sprayed Foam
Materials:
Cementitious • Phenolic • Polyisocyanurate • Polyurethane
Where Applicable:
Enclosed existing wall • Open new wall cavities • Unfinished attic floors
Benefits :
Good for adding insulation to existing finished areas, irregularly shaped areas, and around obstructions.
Structural Insulated Panels (SIPS)
Materials:
Foam board or liquid foam insulation core • Straw core insulation
Where Applicable:
Unfinished walls, ceilings, floors, and roofs for new construction
Benefits :
SIP-built houses provide superior and uniform insulation compared to more traditional construction methods; they also take less time to build.